The majority of the oil used in Spain comes from foreign countries such as Nigeria, the United States, Mexico, Brazil, and Iraq. But, could Spain supply itself? What is the oil market like in Spain? In 1974, the International Energy Agency was created with the aim of coordinating “a collective response” to potential oil supply issues in consumer countries.
It is made up of 28 countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, Republic of Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Additionally, this organization depends on the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), and member countries have minimum oil stock levels stipulated.
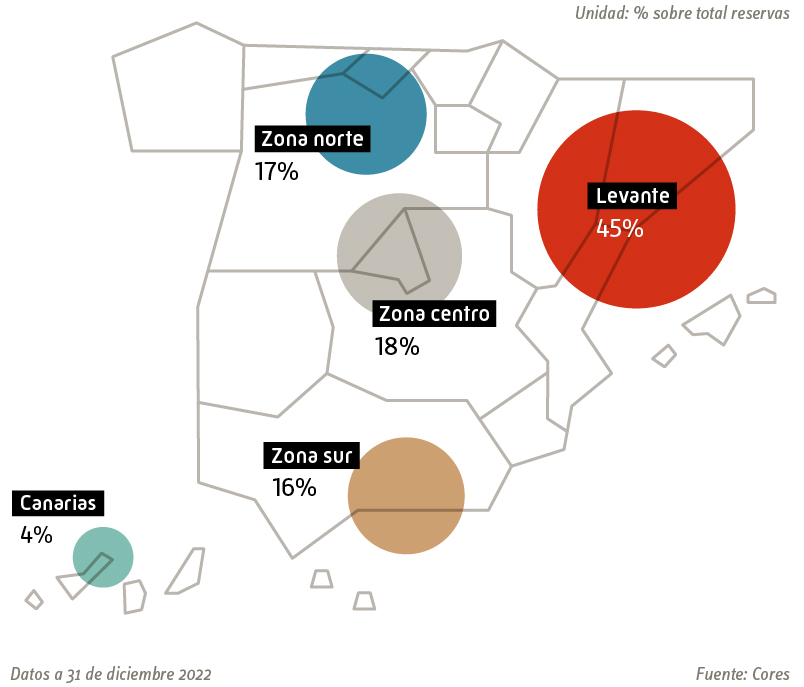
These standards are set to be prepared for potential disruptions in the oil market supply. In the case of Spain, it cannot fall below 90 days of net imports, as detailed by the IEA. Oil reserves are always overseen by a regulatory body, which in our country corresponds to the Strategic Reserves Corporation (CORES).
According to the latest data from the entity, Spain has a total of 113 days of storage. The countries with the largest reserves in the world are Canada and Mexico, which are classified as net exporters. This means that both countries export more than they import. Spain is in a vulnerable position in this regard due to the country’s low oil production. In a year, it only produces 40,000 tons, which translates to 0.07% of its annual consumption, as detailed by the Ministry for the Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenge of Spain.
This requires us to rely on foreign imports to subsist.
Does Spain have oil fields?
In June 2021, Spain closed its doors as an oil-extracting country. After almost 60 years, our country stopped producing oil on the Casablanca platform, located off the coast of Tarragona. The municipality of Ayoluengo, Burgos, was the first Spanish oil field and reached the production of almost 192,000 tons of crude oil, which translates to 0 barrels per day. A figure far from the current situation. After this well, eight more oil fields were discovered. Between 1964 and 2019, Spain had several wells in municipalities such as Ayoluengo, Amposta, Tarraco, or Dorada. Over time, the oil potential has been exploited and has come to an end. The Spanish oil map has been composed of up to ten areas for oil extraction and reached its peak in 1983 with the active extraction of five wells.
From then on, it decreased significantly until the closure of the Casablanca platform, one of the most well-known nationally.
Decline in crude oil storage
Although there is a minimum set by the IEA, sometimes crude oil storage can fall below 90 days. This situation would occur in the case of having to balance prices, as happened in March 2022 due to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Last year, the 31 member countries decided to release up to 60 million barrels to lower the price of a barrel worldwide. This decision was approved in the Council of Ministers, and in the case of Spain, it resulted in the release of 2.6 days of consumption.





